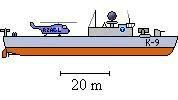
Community Vessel Corvette
| CDF Naval Service Community Vessel | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||
Corvettes are the smallest ships rather than boats in the CDF Naval Service of Sober Thought. They are exclusively dedicated to anti-submarine warfare, whether escorting merchant ships, escorting naval ships or conducting anti-submarine sweeps. They pack nearly as much anti-submarine punch as a frigate with about a third of the crew. Except for a few test and training ships, the Community Defence Forces do not build corvettes in peacetime. These ships are used by the Naval Reserve for training and familiarisation purposes, since the Naval Reserve is primarily responsible for their operation during times of crisis or war.
In wartime, these inexpensive but effective ocean going vessels can be mass produced using assembly line and modular construction techniques. Smaller shipyards can manufacture 14-metre sections, five of which are fitted together to form a single hull. The superstructure is identical to that of the patrol boat and the gun turret the same size as its counterpart on the cruiser-helicopter carrier. Corvettes bear hull numbers in the K series, e.g., K-2, K-9, K-67, and lack official names but get many affectionate and occasionally risque nicknames and semi-official names.
Naval Reserve volunteers make up at least two thirds of the 65-person crew, the remainder filled by Naval Service regular volunteers and fresh Naval Reserve conscripts chosen for their civilian experience as mariners. At least some of the crew ranking Leading Sailor and above are detached from destroyers, frigates or patrol boats; frequently either the CO or XO is a Naval Service regulars.
The Bridge Section has three officers who alternate as officer of the watch: a Lieutenant acting as commanding officer, a Vice Lieutenant as weapons officer and executive officer, and a Vice Lieutenant as engineering officer. The other ranks in the section are a Vice Warrant Officer acting as boat's petty officer, two Leading Sailors, three Master Sailors and nine Sailors.
The Engineering Section, besides its commander, consists of three Leading Sailors, three Master Sailors and nine Sailors. For lack of any more obvious alternative, the Sailor cook and Sailor medic report to the chief engineer as chief of physical plant.
The Naval Weapons Section consists, besides its commander, of thirty all ranks: 5 Leading Sailors, 5 Master Sailors and 20 Sailors. They operate five weapons systems, in declining order of importance for anti-submarine warfare:
- One pair of subsurface missile launchers armed with 48 missiles, stern
- Two torpedo tubes armed with a dozen torpedoes, one on each side of the bow and fore the superstructure
- Two pairs of submarine mortars with 60 depth charges and 40 mini-mines, one pair on each side of the stern
- One twin surface missile launchers armed with 36 missiles, fore of the superstructure
- One anti-aircraft/anti-surface turret with twin 20 mm guns, aft of the bow.
Air component
The corvette carries a single HUBR-77 Hubert ASW naval helicopter on the flight deck aft of the superstructure. When airborne, the helicopter lowers its subsurface sensors by winched cable into the sea. If it senses a submarine, it can fire one or both of its left- and right-facing anti-submarine missile launchers.
The air detachment consists of ten all ranks: a Vice Lieutenant pilot and commanding officer, a Vice Lieutenant co-pilot and executive officer, a Leading Flier head mechanic, a Master Flier crew chief and sensor technician, a Master Flier ordnance technician, two Flier weapons technicians and three Flier mechanics. These are either members of the Air Reserve or seconded from the regular Air Service.