Difference between revisions of "Jeuna"
(→19th century and beyond: fix header level) |
(fix) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
-->{{WIP}} | -->{{WIP}} | ||
| − | + | {{Feedback}} | |
| − | + | ||
<div style="float: right; margin: 0 0 1em 1em; width: auto; text-align: center; font-size: 90%; line-height: 1.4em;"> | <div style="float: right; margin: 0 0 1em 1em; width: auto; text-align: center; font-size: 90%; line-height: 1.4em;"> | ||
<div style="border:1px solid #ccd2d9; width:277px; background:#f9f9f9; text-align:left; padding:0.5em 0em 0em 0em; text-align:center;"> | <div style="border:1px solid #ccd2d9; width:277px; background:#f9f9f9; text-align:left; padding:0.5em 0em 0em 0em; text-align:center;"> | ||
<table style="background:transparent; text-align:left; table-layout:auto; border-collapse:collapse; padding:0; font-size:100%; line-height: 1.2em;" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0"> | <table style="background:transparent; text-align:left; table-layout:auto; border-collapse:collapse; padding:0; font-size:100%; line-height: 1.2em;" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="0"> | ||
| − | <caption style="margin-left:inherit; font-size:135%; padding-bottom:0.5em; line-height:1.1em;">''' | + | <caption style="margin-left:inherit; font-size:135%; padding-bottom:0.5em; line-height:1.1em;">'''妍華共和國<br>''Yánghua Gònghéguó''<br>Republic of Jeuna''' |
</caption> | </caption> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
| Line 30: | Line 29: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| − | <td colspan="2" style="border-top:solid 1px #ccd2d9; vertical-align:top; text-align:center; font-size:95%; padding-top:0.5em; padding-bottom:0.5em;">{{wpl|National anthem|Anthem}}: ''[[Jiāoměi | + | <td colspan="2" style="border-top:solid 1px #ccd2d9; vertical-align:top; text-align:center; font-size:95%; padding-top:0.5em; padding-bottom:0.5em;">{{wpl|National anthem|Anthem}}: ''[[Jiāoměi Yánghua]]'' (娇美妍華)<br/>''Beautiful and Graceful Jeuna''</td> |
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td colspan="2" style="border-top:solid 1px #ccd2d9; vertical-align:top; text-align:left; font-size:95%;"><br /> | <td colspan="2" style="border-top:solid 1px #ccd2d9; vertical-align:top; text-align:left; font-size:95%;"><br /> | ||
| Line 157: | Line 156: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| − | '''Jeuna''', officially the '''Republic of Jeuna''' (known in {{wpl|Chinese language|Chinese}} as | + | '''Jeuna''', officially the '''Republic of Jeuna''' (known in {{wpl|Chinese language|Chinese}} as 妍華共和國; {{wpl|pinyin}}: ''Yánghua Gònghéguó'') is a {{wpl|country}} in {{wpl|East Asia}} (commonly considered part of {{wpl|Manchuria}}). It is bordered to the north and east by {{wpl|Russia}} and to the south and west by the {{wpl|People's Republic of China}}. |
== Etymology == | == Etymology == | ||
| − | Jeuna is usually known as '''''Yuánguó''''' ({{wpl|Chinese language|Chinese}}: | + | Jeuna is usually known as '''''Yuánguó''''' ({{wpl|Chinese language|Chinese}}: 妍國) in {{wpl|Mandarin Chinese}}. The first character, 妍, means 'beautiful', while the second character, 國, means 'state' or 'country'. {{wpl|Christian}} missionaries originally translated the name as 'Beautiful Kingdom'. |
| − | The origin of the English construct 'Jeuna' may have come from two sources. The first is that 'Jeuna' was derived from {{wpl|Sanskrit}} ''Jun'', which referenced the Jin Dynasty that ruled the area. Traders on the {{wpl|Silk Road}} may have identified themselves as such. The other possibility is that 'Jeuna' is a corruption of the original name, '' | + | The origin of the English construct 'Jeuna' may have come from two sources. The first is that 'Jeuna' was derived from {{wpl|Sanskrit}} ''Jun'', which referenced the Jin Dynasty that ruled the area. Traders on the {{wpl|Silk Road}} may have identified themselves as such. The other possibility is that 'Jeuna' is a corruption of the original name, ''Yánghua''. |
== History == | == History == | ||
| Line 189: | Line 188: | ||
{{main|Military of Jeuna}} | {{main|Military of Jeuna}} | ||
| − | Jeuna possesses a small military force, which | + | Jeuna possesses a small military force, which has evolved from being dependent on {{wpl|United States}} hardware to being almost entirely self-sufficient. It is composed of two branches, which are the [[Jeunese Republican Guard|Republican Guard]] and the [[Jeunese Air Defence Force]]. |
| − | + | The Republican Guard also operates several riverine defence vessels for patrolling the {{wpl|Amur River}} and its tributaries. These vessels are organised into the [[Republican Guard River Defence Force]]. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ==Administrative divisions== | |
| − | + | ||
| − | == Administrative divisions == | + | |
{{main|Administrative divisions of Jeuna}} | {{main|Administrative divisions of Jeuna}} | ||
| − | Jeuna is divided into | + | Jeuna is divided into thirteen [[Administrative divisions of Jeuna#Province-level|province-level divisions]], consisting of twelve province-level cities and one province: |
| + | |||
| + | * [[Harbin]] {{wpl|Simplified Chinese}}: 哈尔滨市, {{wpl|Hanyu Pinyin}}: Hā'ěrbīn shì) | ||
| + | * [[Qiqihar]] (齐齐哈尔市 Qíqíhā'ěr shì) | ||
| + | * [[Hegang]] (鹤岗市 Hègǎng shì) | ||
| + | * [[Shuangyashan]] (双鸭山市 Shuāngyāshān shì) | ||
| + | * [[Jixi]] (鸡西市 Jīxī shì) | ||
| + | * [[Daqing]] (大庆市 Dàqìng shì) | ||
| + | * [[Yichun, Heilongjiang|Yichun]] (伊春市 Yīchūn shì) | ||
| + | * [[Mudanjiang]] (牡丹江市 Mǔdānjiāng shì) | ||
| + | * [[Jiamusi]] (佳木斯市 Jiāmùsī shì) | ||
| + | * [[Qitaihe]] (七台河市 Qītáihé shì) | ||
| + | * [[Heihe]] (黑河市 Hēihé shì) | ||
| + | * [[Suihua]] (绥化市 Suíhuà shì) | ||
| + | * [[Greater Khingan province|Daxing'anling Province]] (大兴安岭地区 Dàxīng'ānlǐng Dìqū){{ref|province}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The thirteen province-level divisions of Jeuna are subdivided into 130 [[Administrative divisions of Jeuna#County-level|county-level divisions]] (65 [[Political divisions of Jeuna#District-level|district]]s, nineteen [[county-level cities]], forty-five [[Political divisions of Jeuna#County-level|counties]], and one [[autonomous county]]). Those are in turn divided into 1,284 [[Political divisions of Jeuna#Township-level|township-level divisions]] (473 [[Political divisions of Jeuna#Town-level|town]]s, 400 [[Political divisions of Jeuna#Township-level|township]]s, 58 [[ethnic township]]s, and 353 [[subdistrict]]s). | ||
| + | |||
| + | See '''[[Administrative divisions of Jeuna]]''' for a complete list of [[Administrative divisions of Jeuna#County-level|county-level divisions]]. | ||
== Geography == | == Geography == | ||
{{main|Geography of Jeuna}} | {{main|Geography of Jeuna}} | ||
| − | Jeuna is a land of varied topography. Much of the | + | Jeuna is a land of varied topography. Much of the country is dominated by mountain ranges such as the {{wpl|Greater Khingan}} Range and {{wpl|Lesser Khingan}} Range, {{wpl|Zhangguangcai Mountains}}, {{wpl|Laoye Mountains}}, and {{wpl|Wanda Mountains}}. The highest peak is {{wpl|Mount Datudingzi}} at 1690 {{wpl|Metre|m}} (5545 {{wpl|foot (unit of length)|ft}}), located on the border with the {{wpl|People's Republic of China}}). The Greater Khingan Range contains Jeuna's largest remaining virgin forest and is an important area for Jeuna's forestry industry. |
[[Image:Ice_Snow_World.jpg|thumb|300px|Winter night in [[Harbin]]'s Ice and Snow World.]] | [[Image:Ice_Snow_World.jpg|thumb|300px|Winter night in [[Harbin]]'s Ice and Snow World.]] | ||
| Line 224: | Line 237: | ||
== Economy == | == Economy == | ||
{{main|Economy of Jeuna}} | {{main|Economy of Jeuna}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Jeuna's economy has been rapidly transformed in recent years from a system largely dependant on agriculture and logging industries to one that is widely-diversified and technologically advanced. Jeuna has the world's 13th largest economy and Asia's 4th's largest (ranking 3rd in Asia and 11th in the world in {{wpl|purchasing power parity}}); it is one of the Five Asian Tigers. One of Jeuna's major buyers is the {{wpl|People's Republic of China}}.<!-- | ||
| + | |||
| + | More to come. | ||
| + | |||
| + | --> | ||
== Demographics == | == Demographics == | ||
| + | The majority of Jeuna's population is {{wpl|Han Chinese}}, while other {{wpl|List of Chinese nationalities|ethnic minorities}} include the {{wpl|Manchu}}s, {{wpl|Koreans}}, {{wpl|Mongol}}s, {{wpl|Hui people|Hui}}, {{wpl|Daur}}, {{wpl|Xibe}}, {{wpl|Oroqin}}, {{wpl|Hezhen}} and {{wpl|Russians}}. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:right;" | ||
| + | ! colspan="3" | Ethnic groups in Jeuna (2007 estimate){{ref|ethnic}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Nationality !! Population !! Percentage | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | {{wpl|Han Chinese}} || 64,054,673 || 95.20% | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | {{wpl|Manchu}} || 1,924,332 || 2.86% | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | {{wpl|Koreans}} || 719,942 || 1.07% | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | {{wpl|Mongol}} || 262,409 || 0.39% | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | {{wpl|Hui people|Hui}} || 228,767 || 0.34% | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | {{wpl|Daur}} || 80,741 || 0.12% | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | {{wpl|Xibe}} || 20,185 || 0.03% | ||
| + | |} | ||
== Culture == | == Culture == | ||
{{main|Jeunese culture}} | {{main|Jeunese culture}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == References and notes == | ||
| + | {| style="font-size:90%;" | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | #{{note|province}} More information at {{wpl|Greater Khighan}}. | ||
| + | #{{note|ethnic}} Based on percentages from the 2006 census. | ||
| + | |} | ||
[[Category:Jeuna| ]] | [[Category:Jeuna| ]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:07, 15 October 2007
This article is incomplete because it is pending further input from participants, or it is a work-in-progress by one author.
Please comment on this article's talk page to share your input, comments and questions.
Note: To contribute to this article, you may need to seek help from the author(s) of this page.
- The below template has been nominated for deletion. Please see its talk page to comment.
After reading the article, please comment on Jeuna's talk page to contribute to the discussion.
|
Anthem: Jiāoměi Yánghua (娇美妍華) Beautiful and Graceful Jeuna |
||||
| Capital (and largest city) |
Harbin |
||||
| Official language | Chinese1 | ||||
| Government | Parliamentary republic | ||||
| - President | Fan Banou | ||||
| - Premier | Jin Jiahua | ||||
| Formation | |||||
| - National Formation Day | 7 September, 1211 | ||||
| - Independence from China |
18 August, 1921 | ||||
| Area | |||||
| - Total | 460,000 km² (55th) | ||||
| 177,607 sq mi | |||||
| - Water (%) | 1.74 | ||||
| Population | |||||
| - 2007 estimate | 67,284,320 (19th) | ||||
| - Density | 146 /km² (68th) | ||||
| 379 /sq mi | |||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2007 estimate | ||||
| - Total | $1.57 trillion (11th) | ||||
| - Per capita | $23,350 (33rd) | ||||
| HDI (2003) |  0.912 (high) (27th) 0.912 (high) (27th) |
||||
| Currency | Yin (international Ỵ, Chinese 银, yín) (JNY) |
||||
| Time zone | JST (UTC+9) | ||||
| - Summer (DST) | not observed (UTC+9) | ||||
| Internet TLD | .jn | ||||
| Calling code | +83 | ||||
| 1De facto official. | |||||
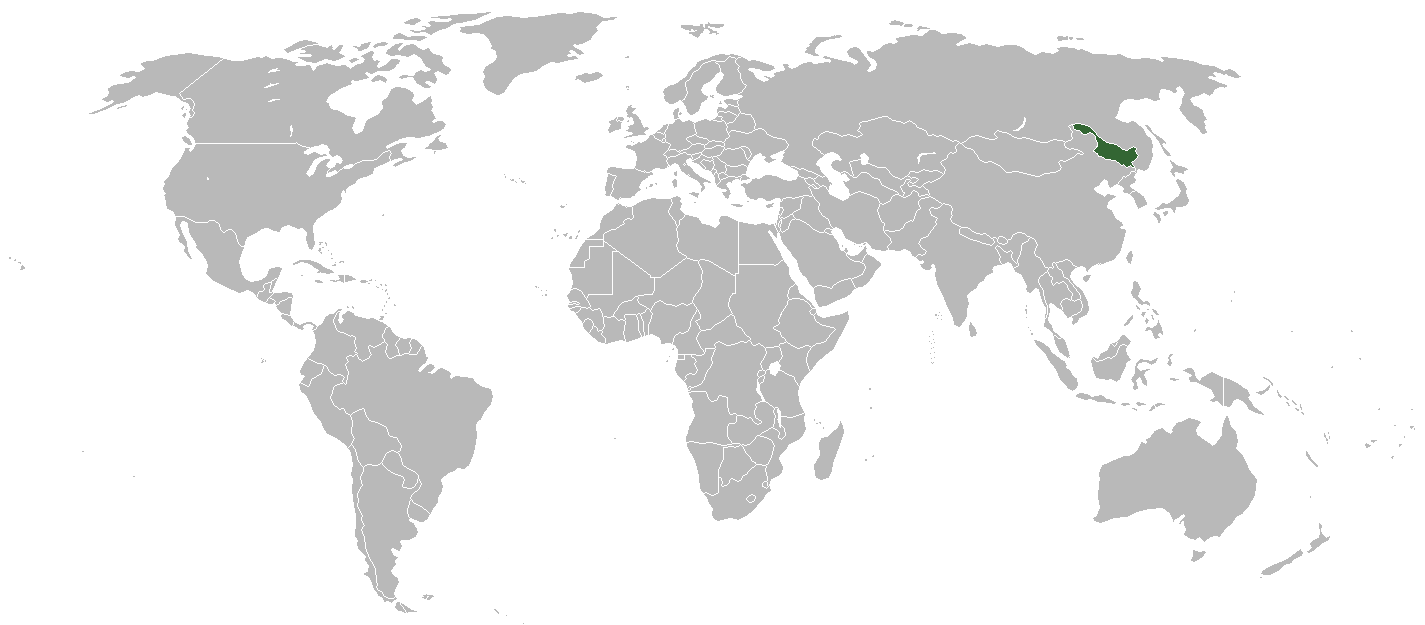
Jeuna, officially the Republic of Jeuna (known in Chinese as 妍華共和國; pinyin: Yánghua Gònghéguó) is a country in East Asia (commonly considered part of Manchuria). It is bordered to the north and east by Russia and to the south and west by the People's Republic of China.
Contents
Etymology
Jeuna is usually known as Yuánguó (Chinese: 妍國) in Mandarin Chinese. The first character, 妍, means 'beautiful', while the second character, 國, means 'state' or 'country'. Christian missionaries originally translated the name as 'Beautiful Kingdom'.
The origin of the English construct 'Jeuna' may have come from two sources. The first is that 'Jeuna' was derived from Sanskrit Jun, which referenced the Jin Dynasty that ruled the area. Traders on the Silk Road may have identified themselves as such. The other possibility is that 'Jeuna' is a corruption of the original name, Yánghua.
History
- Main article(s): History of Jeuna
Early Jeuna
Jeuna's history stretches back as far as the fifth century, when it was first known to be inhabited by such people as the Xianbei, the Mohe, and the Khitan. The eastern portion of Jeuna was ruled by kingdom of Bohai between the 7th century and 10th century. The Jurchen Jin Dynasty (1115-1234) that subsequently ruled much of northern China arose within the borders of modern Jeuna.
Under the Manchu Qing Dynasty, the western part of Jeuna was under the supervision of the General of Heilongjiang (its name under Chinese rule), whose power extended, according to the Treaty of Nerchinsk, as far north as the Stanovoy Mountains; eastern Jeuna was under the supervision of the General of Jilin, whose power reached the Sea of Japan. These areas deep in Manchuria were closed off to Han Chinese migration.
19th century and beyond
However, in 1858 and 1860 the Qing government gave up all land beyond the Amur and Ussuri Rivers to Russia, cutting China off from the Sea of Japan and giving Jeuna its present northern borders. At the same time, Manchuria was opened to Han Chinese migration by the Qing government. By the early twentieth century, the Han Chinese had become the dominant ethnic group in the region. Foreign rule over the region ended in 1911 with the fall of the Qing Dynasty, and in 1921 formalised its independence with the codification of a constitution.
In 1922, Soviet-backed guerilla forces waged a war to establish a communist-style government in Jeuna, whose progress was stalled by secret United States intervention. The rebels were eventually put down, and Jeuna became an unofficial ally of the US; it formalised this relationship with the adoption of the Treaty of Harbin in 1931.
Government and politics
- Main article(s): Government of Jeuna
Foreign relations
- Main article(s): Foreign relations of Jeuna
Jeuna maintains a strong relationship with the United States, and has historically disagreed with both the People's Republic of China and North Korea since their communist revolutions. For a time, Jeuna was an important strategic foothold against the USSR, and several bases were built in the north and eastern areas of the country as a precautionary measure to stave off invasions by the Soviets.
Military
- Main article(s): Military of Jeuna
Jeuna possesses a small military force, which has evolved from being dependent on United States hardware to being almost entirely self-sufficient. It is composed of two branches, which are the Republican Guard and the Jeunese Air Defence Force.
The Republican Guard also operates several riverine defence vessels for patrolling the Amur River and its tributaries. These vessels are organised into the Republican Guard River Defence Force.
Administrative divisions
- Main article(s): Administrative divisions of Jeuna
Jeuna is divided into thirteen province-level divisions, consisting of twelve province-level cities and one province:
- Harbin Simplified Chinese: 哈尔滨市, Hanyu Pinyin: Hā'ěrbīn shì)
- Qiqihar (齐齐哈尔市 Qíqíhā'ěr shì)
- Hegang (鹤岗市 Hègǎng shì)
- Shuangyashan (双鸭山市 Shuāngyāshān shì)
- Jixi (鸡西市 Jīxī shì)
- Daqing (大庆市 Dàqìng shì)
- Yichun (伊春市 Yīchūn shì)
- Mudanjiang (牡丹江市 Mǔdānjiāng shì)
- Jiamusi (佳木斯市 Jiāmùsī shì)
- Qitaihe (七台河市 Qītáihé shì)
- Heihe (黑河市 Hēihé shì)
- Suihua (绥化市 Suíhuà shì)
- Daxing'anling Province (大兴安岭地区 Dàxīng'ānlǐng Dìqū)[1]
The thirteen province-level divisions of Jeuna are subdivided into 130 county-level divisions (65 districts, nineteen county-level cities, forty-five counties, and one autonomous county). Those are in turn divided into 1,284 township-level divisions (473 towns, 400 townships, 58 ethnic townships, and 353 subdistricts).
See Administrative divisions of Jeuna for a complete list of county-level divisions.
Geography
- Main article(s): Geography of Jeuna
Jeuna is a land of varied topography. Much of the country is dominated by mountain ranges such as the Greater Khingan Range and Lesser Khingan Range, Zhangguangcai Mountains, Laoye Mountains, and Wanda Mountains. The highest peak is Mount Datudingzi at 1690 m (5545 ft), located on the border with the People's Republic of China). The Greater Khingan Range contains Jeuna's largest remaining virgin forest and is an important area for Jeuna's forestry industry.
The interior of the country, which is relatively flat and low in altitude, contains the Songhua River, the Nen River, and the Mudan River, all tributaries of the Amur, while the northern border forms part of the Amur valley. Xingkai Lake (or Khanka Lake) is found on the border with Russia's Primorsky Krai.
Jeuna is subarctic in climate. Winters are long and frigid, with an average of −31 to −15°C in January, and summers are short and cool with an average of 18 to 23°C in July. The annual average rainfall is 500 to 600 mm, concentrated mostly in summer.
Major cities:
Economy
- Main article(s): Economy of Jeuna
Jeuna's economy has been rapidly transformed in recent years from a system largely dependant on agriculture and logging industries to one that is widely-diversified and technologically advanced. Jeuna has the world's 13th largest economy and Asia's 4th's largest (ranking 3rd in Asia and 11th in the world in purchasing power parity); it is one of the Five Asian Tigers. One of Jeuna's major buyers is the People's Republic of China.
Demographics
The majority of Jeuna's population is Han Chinese, while other ethnic minorities include the Manchus, Koreans, Mongols, Hui, Daur, Xibe, Oroqin, Hezhen and Russians.
| Ethnic groups in Jeuna (2007 estimate)[2] | ||
|---|---|---|
| Nationality | Population | Percentage |
| Han Chinese | 64,054,673 | 95.20% |
| Manchu | 1,924,332 | 2.86% |
| Koreans | 719,942 | 1.07% |
| Mongol | 262,409 | 0.39% |
| Hui | 228,767 | 0.34% |
| Daur | 80,741 | 0.12% |
| Xibe | 20,185 | 0.03% |
Culture
- Main article(s): Jeunese culture
References and notes
|